Greenhouse Gas Reductions
 Sugarcane is a low-carbon building block that can be used to produce a wide range of clean and renewable products.
Sugarcane is a low-carbon building block that can be used to produce a wide range of clean and renewable products.
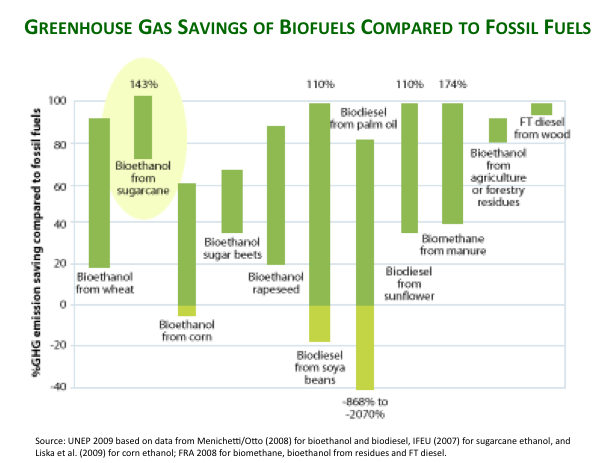
Probably the most recognized is sugarcane ethanol which reduces greenhouse gas emissions by 90 percent on average compared to gasoline. That’s the best carbon performance of any biofuel produced at commercial scale. Learn more about sugarcane ethanol’s evaluation and designation by leading environmental regulators in the United States and European Union.
Other sugarcane products offer similar low-carbon advantages. Several factors explain why sugarcane can reduce greenhouse gases so significantly compared to other alternatives:
- Carbon Stocks
In sugarcane fields, carbon stocks amount to 60 tons of carbon per hectare (including above and below ground and soil organic carbon). It means that a lot of carbon is stored in small portions of land, allowing for higher greenhouse gas reductions from the products produced in that area. - Semi-Perennial Plant.
Sugarcane only needs to be replanted about every six years which reduces tilling of land that releases carbon dioxide. No-till techniques are also strongly encouraged, considerably lowering the amount of fuel necessary to run agricultural machinery in the field. - Limited Chemical Use.
The application of pesticides in Brazilian sugarcane fields is low and the use of fungicides practically nonexistent. Major diseases that threaten sugarcane are fought through biological control and advanced genetic enhancement programs. Brazilian sugarcane growers also apply relatively few industrialized fertilizers, due to the innovative use of organic fertilizers from recycled production residues.All of it reduces the demand for fossil-based products, improving sugarcane ethanol’s greenhouse benefits. - Bioelectricity.
Sugarcane mills are energy self-sufficient. They burn leftover stalks and leaves in boilers to produce enough bioelectricity to power their operations and often sell energy back to the grid. Producers can also obtain carbon credits from bioelectricity project. - Yields.
Each hectare of sugarcane produces more than 7,000 liters of ethanol. It means that with less input, including fossil one, more energy is produced. It boosts greenhouse gas reduction benefits of sugarcane-based products.
Since 2003, Brazil’s use of sugarcane ethanol has reduced that country’s emissions of carbon dioxide by more than 535 million tons. That’s as good for the environment as planting and maintaining 4 billion trees for 20 years! These low-carbon benefits from sugarcane will expand with greater production and use of other products like cellulosic ethanol, bioplastics and biohydrocarbons.
You May Also Be Interested In...
Sustainability Certification & Reporting
OVERVIEW VIDEO